|
I am a Sr. Director of Vision and Robotics at United Imaging Intelligence (UII America) in Boston, MA, where I work on computer vision, machine learning and robotics problems in medical environments. Before joining UII I have worked at Siemens Corporate Research in Princeton, NJ and Honeywell Technology Solutions Labs in Shanghai, China respectively. I received my PhD in Computer and Systems Engineering from Department of Electrical, Computer, and Systems Engineering of Rensselaer Polytechnic Institute in May 2014 under the guidance of Prof. Richard J. Radke. |
 |
|
| My research interests are computer vision and machine learning, with special focus on human pose and shape estimation, explainable AI, object detection and tracking, anomaly detection, augmented reality, scene understanding, human re-identification and camera calibration. |

|
We propose Seq2Time, a data-oriented training paradigm that leverages sequences of images and short video clips to enhance temporal awareness in long videos. By converting sequence positions into temporal annotations, we transform largescale image and clip captioning datasets into sequences that mimic the temporal structure of long videos, enabling self-supervised training with abundant time-sensitive data. To enable sequence-to-time knowledge transfer, we introduce a novel time representation that unifies positional information across image sequences, clip sequences, and long videos. |

|
Novel view synthesis has advanced significantly with the development of neural radiance fields (NeRF) and 3D Gaussian splatting (3DGS). However, achieving high quality without compromising real-time rendering remains challenging, particularly for physically-based ray tracing with view-dependent effects.We introduce 6D Gaussian Splatting (6DGS), which enhances color and opacity representations and leverages the additional directional information in the 6D space for optimized Gaussian control. Our approach is fully compatible with the 3DGS framework and significantly improves real-time radiance field rendering by better modeling view-dependent effects and fine details. |

|
We propose a solution that adequately handles the distinct visual and semantic modalities, i.e., a 3D vision-language Gaussian splatting model for scene understanding, to put emphasis on the representation learning of language modality. We propose a novel cross-modal rasterizer, using modality fusion along with a smoothed semantic indicator for enhancing semantic rasterization. We also employ a camera-view blending technique to improve semantic consistency between existing and synthesized views, thereby effectively mitigating over-fitting. |

|
We introduce a novel order-aware attention, where the order maps seamlessly guide the user interactions (in the form of clicks) to attend to the image features. We further present an object-aware attention module to incorporate a strong object-level understanding to better differentiate objects with similar order. Our approach allows both dense and sparse integration of user clicks, enhancing both accuracy and efficiency as compared to prior works. |

|
We propose an automated patient positioning system that utilizes a camera to detect specific hand gestures from technicians, allowing users to indicate the target patient region to the system and initiate automated positioning. Our approach relies on a novel multi-stage pipeline to recognize and interpret the technicians’ gestures, translating them into precise motions of medical devices. *Equal Contributions |

|
We present a novel approach that marries realistic physics-inspired X-ray simulation with efficient, differentiable DRR generation using 3D Gaussian splatting (3DGS). Our direction-disentangled 3DGS (DDGS) method separates the radiosity contribution into isotropic and direction-dependent components, approximating complex anisotropic interactions without intricate runtime simulations. Additionally, we adapt the 3DGS initialization to account for tomography data properties, enhancing accuracy and efficiency. *Equal Contributions |

|
We introduce a novel bottom-up approach for human body mesh reconstruction, specifically designed to address the challenges posed by partial visibility and occlusion in input images. Our method reconstructs human body parts independently before fusing them, thereby ensuring robustness against occlusions. We design Human Part Parametric Models that independently reconstruct the mesh from a few shape and global-location parameters, without inter-part dependency. A specially designed fusion module then seamlessly integrates the reconstructed parts, even when only a few are visible. |

|
We present MSFSeg, a novel few-shot 3D segmentation framework with a lightweight multi-surrogate fusion (MSF). MSFSeg is able to automatically segment unseen 3D objects/organs (during training) provided with one or a few annotated 2D slices or 3D sequence segments, via learning dense query-support organ/lesion anatomy correlations across patient populations. Our proposed MSF module mines comprehensive and diversified morphology correlations between unlabeled and the few labeled slices/sequences through multiple designated surrogates, making it able to generate accurate cross-domain 3D segmentation masks given annotated slices or sequences. |

|
This work addresses the issue of cross-class domain adaptation (CCDA) in semantic segmentation, where the target domain contains both shared and novel classes that are either unlabeled or unseen in the source domain. We propose a label alignment method by leveraging VLMs to relabel pseudo labels for novel classes. We embed a two-stage method to enable fine-grained semantic segmentation and design a threshold based on the uncertainty of pseudo labels to exclude noisy VLM predictions. To further augment the supervision of novel classes, we devise memory banks with an adaptive update scheme to effectively manage accurate VLM predictions, which are then resampled to increase the sampling probability of novel classes. |
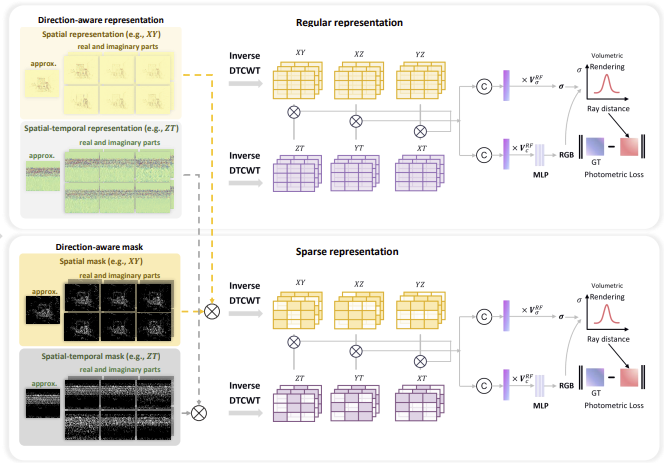
|
We present a novel direction-aware representation (DaRe) approach that captures scene dynamics from six different directions. This learned representation undergoes an inverse dual-tree complex wavelet transformation (DTCWT) to recover plane-based information. DaReNeRF computes features for each space-time point by fusing vectors from these recovered planes. Combining DaReNeRF with a tiny MLP for color regression and leveraging volume rendering in training yield state-of-the-art performance in novel view synthesis for complex dynamic scenes. Notably, to address redundancy introduced by the six real and six imaginary direction-aware wavelet coefficients, we introduce a trainable masking approach, mitigating storage issues without significant performance decline. |

|
The official proceedings of the Second Workshop on Artificial Intelligence with Biased or Scarce Data in conjunction with AAAI Conference on Artificial Intelligence 2024. |
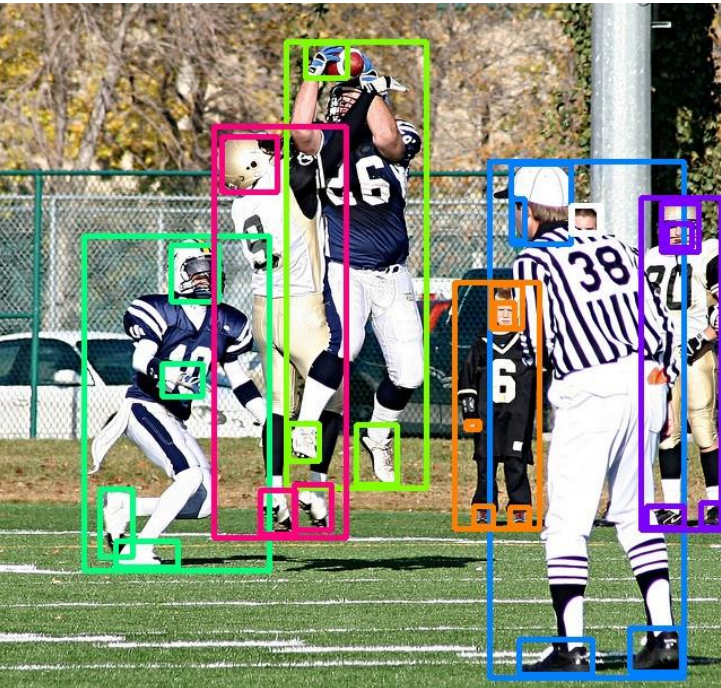
|
We presents PBADet, a novel one-stage, anchor-free approach for part-body association detection. Building upon the anchor-free object representation across multi-scale feature maps, we introduce a singular part-to-body center offset that effectively encapsulates the relationship between parts and their parent bodies. Our design is inherently versatile and capable of managing multiple parts-to-body associations without compromising on detection accuracy or robustness. |
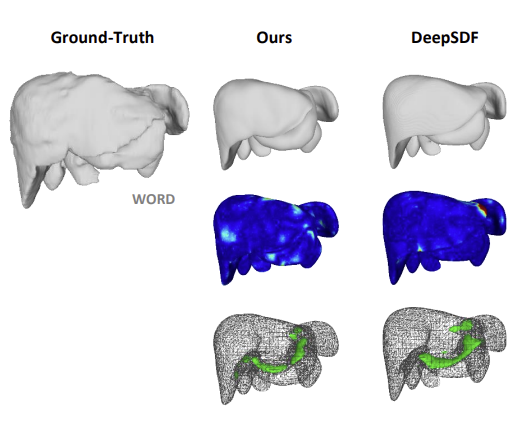
|
In this work, we propose MODIF, a multi-object deep implicit function that jointly learns the deformation fields and instance-specific latent codes for multiple objects at once. Our emphasis is on non-rigid, non-interpenetrating entities such as organs. To effectively capture the interrelation between these entities and ensure precise, collision-free representations, our approach facilitates signaling between category-specific fields to adequately rectify shapes. We also introduce novel inter-object supervision: an attraction-repulsion loss is formulated to refine contact regions between objects. |

|
In this paper, we introduce Disguise, a novel algorithm that seamlessly de-identifies facial images while ensuring the usability of the modified data. Unlike previous approaches, our solution is firmly grounded in the domains of differential privacy and ensemble-learning research. Our method involves extracting and substituting depicted identities with synthetic ones, generated using variational mechanisms to maximize obfuscation and non-invertibility. Additionally, we leverage supervision from a mixture-of-experts to disentangle and preserve other utility attributes. |
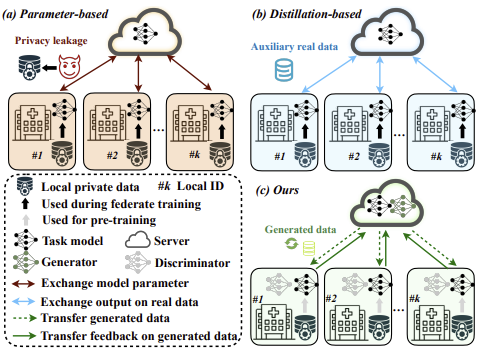
|
We propose a federated learning framework eliminating any requirement of recursive local parameter exchange or auxiliary task-relevant data to transfer knowledge, thereby giving direct privacy control to local users. In particular, to cope with the inherent data heterogeneity across locals, our technique learns to distill input on which each local model produces consensual yet unique results to represent each expertise. |
|
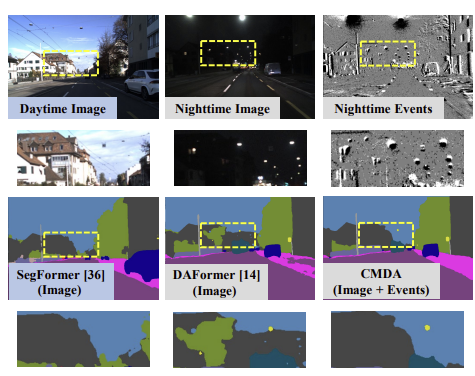
Event cameras, as a new form of vision sensors, are complementary to conventional cameras with their high dynamic range. To this end, we propose a novel unsupervised Cross-Modality Domain Adaptation (CMDA) framework to leverage multi-modality (Images and Events) information for nighttime semantic segmentation, with only labels on daytime images. |
|
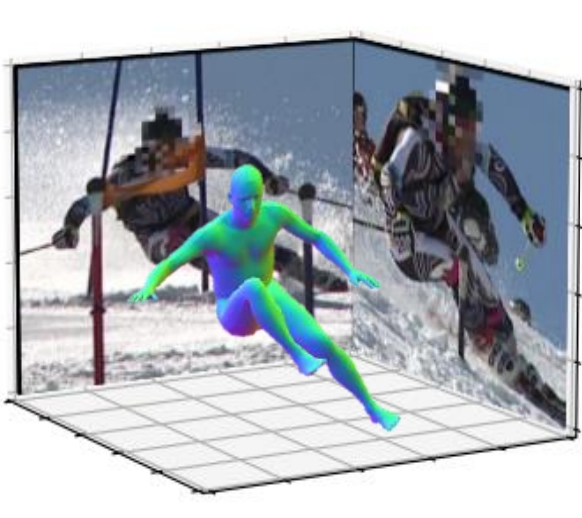
We propose a novel simulation-based training pipeline for multi-view human mesh recovery, which (a) relies on intermediate 2D representations which are more robust to synthetic-to-real domain gap; (b) leverages learnable calibration and triangulation to adapt to more diversified camera setups; and (c) progressively aggregates multi-view information in a canonical 3D space to remove ambiguities in 2D representations. |
|
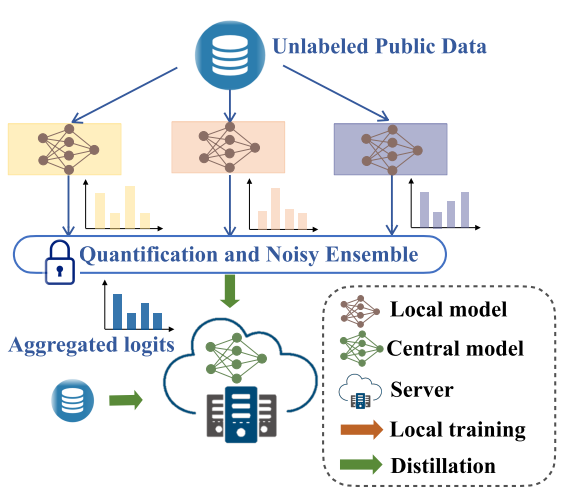
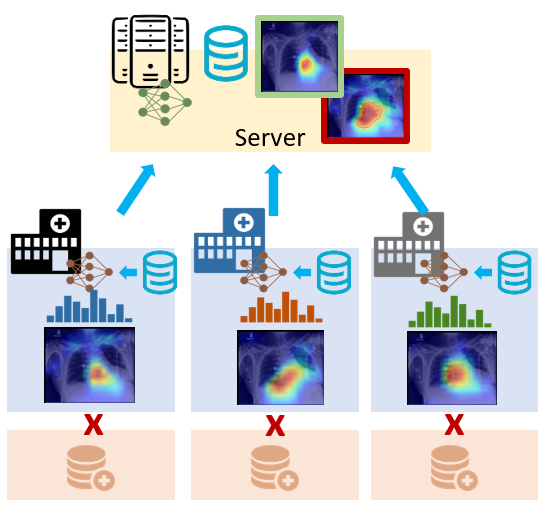
We propose a privacy-preserving FL framework leveraging unlabeled public data for one-way offline knowledge distillation in this work. The central model is learned from local knowledge via ensemble attention distillation. Our technique uses decentralized and heterogeneous local data like existing FL approaches, but more importantly, it significantly reduces the risk of privacy leakage. We demonstrate that our method achieves very competitive performance with more robust privacy preservation based on extensive experiments on image classification, segmentation, and reconstruction tasks. |
|
|
The moving patterns of human in a constrained scenario typically conform to a limited number of regularities to a certain extent, because of the scenario restrictions and person-person or person-object interactivity. We propose to forecast a person's future trajectory by learning from the implicit scene regularities. We call the regularities, inherently derived from the past dynamics of the people and the environment in the scene, scene history. We introduce a novel framework Scene History Excavating Network (SHENet), where the scene history is leveraged in a simple yet effective approach. |
|
|
We leverage a neural motion field for estimating the motion of all points in a multiview setting. Modeling the motion from a dynamic scene with multiview data is challenging due to the ambiguities in points of similar color and points with time-varying color. We propose to regularize the estimated motion to be predictable. If the motion from previous frames is known, then the motion in the near future should be predictable. Therefore, we introduce a predictability regularization by first conditioning the estimated motion on latent embeddings, then by adopting a predictor network to enforce predictability on the embeddings. |
|
|
We propose cross-representation alignment utilizing the complementary information from the robust but sparse representation (2D keypoints). Specifically, the alignment errors between initial mesh estimation and both 2D representations are forwarded into regressor and dynamically corrected in the following mesh regression. This adaptive cross-representation alignment explicitly learns from the deviations and captures complementary information: robustness from sparse representation and richness from dense representation. |
|
|
We ask the question: can our model directly predict where to click, so as to further reduce the user interaction cost? To this end, we propose PseudoClick, a generic framework that enables existing segmentation networks to propose candidate next clicks. These automatically generated clicks, termed pseudo clicks in this work, serve as an imitation of human clicks to refine the segmentation mask. We build PseudoClick on existing segmentation backbones and show how our click prediction mechanism leads to improved performance. |
|
|
We propose a generic modularized 3D patient modeling method consists of (a) a multi-modal keypoint detection module with attentive fusion for 2D patient joint localization, to learn complementary cross-modality patient body information, leading to improved keypoint localization robustness and generalizability in a wide variety of imaging and clinical scenarios; and (b) a self-supervised 3D mesh regression module which does not require expensive 3D mesh parameter annotations to train, bringing immediate cost benefits for clinical deployment. |
|
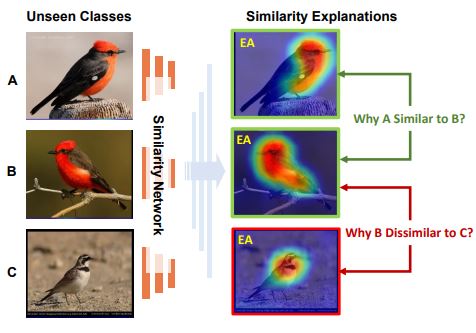
We propose the first method to generate generic visual similarity explanations with gradient-based attention. We demonstrate that our technique is agnostic to the specific similarity model type, e.g., we show applicability to Siamese, triplet, and quadruplet models. Furthermore, we make our proposed similarity attention a principled part of the learning process, resulting in a new paradigm for learning similarity functions. We demonstrate that our learning mechanism results in more generalizable, as well as explainable, similarity models. |

|
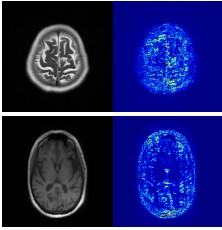
We present the first learning-based approach to estimate the patient’s internal organ deformation for arbitrary human poses in order to assist with radiotherapy and similar medical protocols. The underlying method first leverages medical scans to learn a patient-specific representation that potentially encodes the organ’s shape and elastic properties. During inference, given the patient’s current body pose information and the organ's representation extracted from previous medical scans, our method can estimate their current organ deformation to offer guidance to clinicians. |

|
The official proceedings of the First Workshop on Artificial Intelligence with Biased or Scarce Data in conjunction with AAAI Conference on Artificial Intelligence 2022. |
|
We propose a quantized and noisy ensemble of local predictions from completely trained local models for stronger privacy guarantees without sacrificing accuracy. Based on extensive experiments on classification and segmentation tasks, we show that our method outperforms baseline FL algorithms with superior performance in both accuracy and data privacy preservation. |
|
|
We propose a Multi-motion and Appearance Self-supervised Network (MASNet) to introduce multi-scale motion information and appearance information of scene for MOD. Introducing multi-scale motion can aggregate these regions to form a more complete detection. Appearance information can serve as another cue for MOD when the motion independence is not reliable and for removing false detection in background caused by locally independent background motion. |

|
We present a generalized human mesh optimization algorithm that substantially improves the performance of existing methods on both obese person images as well as community-standard benchmark datasets. The proposed method utilizes only 2D annotations without relying on supervision from expensive-to-create mesh parameters. |
|
|
|
|
We propose a new distillation-based FL framework that can preserve privacy by design, while also consuming substantially less network communication resources when compared to the current methods. Our framework engages in inter-node communication using only publicly available and approved datasets, thereby giving explicit privacy control to the user. To distill knowledge among the various local models, our framework involves a novel ensemble distillation algorithm that uses both final prediction as well as model attention. |
|
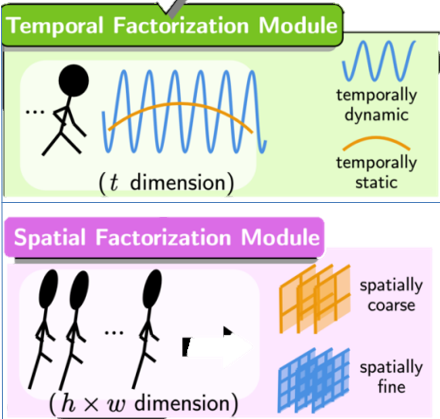
We propose Spatio-Temporal Representation Factorization (STRF), a flexible new computational unit that can be used in conjunction with most existing 3D convolutional neural network architectures for re-ID. The key innovations of STRF over prior work include explicit pathways for learning discriminative temporal and spatial features, with each component further factorized to capture complementary person-specific appearance and motion information. Specifically, temporal factorization comprises two branches, one each for static features (e.g., the color of clothes) that do not change much over time, and dynamic features (e.g., walking patterns) that change over time. |
|
|
We propose a novel framework to interpret neural networks which extracts relevant class-specific visual concepts and organizes them using structural concepts graphs based on pairwise concept relationships. By means of knowledge distillation, we show VRX can take a step towards mimicking the reasoning process of NNs and provide logical, concept-level explanations for final model decisions. With extensive experiments, we empirically show VRX can meaningfully answer “why” and “why not” questions about the prediction, providing easy-to-understand insights about the reasoning process. We also show that these insights can potentially provide guidance on improving NN’s performance. |
|
|
We proposed zero-shot deep domain adaptation (ZDDA). ZDDA-C/ML learns to generate common representations for source and target domains data. Then, either domain representation is used later to train a system that works on both domains or having the ability to eliminate the need to either domain in sensor fusion settings. In this paper, two variants of ZDDA have been developed for classification and metric learning task respectively. |
|
|
We propose a new attention-driven weakly supervised algorithm comprising a hierarchical attention mining framework that unifies activation- and gradient-based visual attention in a holistic manner. Our key algorithmic innovations include the design of explicit ordinal attention constraints, enabling principled model training in a weakly-supervised fashion, while also facilitating the generation of visual-attention-driven model explanations by means of localization cues. |
|
|
This paper considers the problem of 3D patient body modeling. Such a 3D model provides valuable information for improving patient care, streamlining clinical workflow, automated parameter optimization for medical devices etc. We present a novel robust dynamic fusion technique that facilitates flexible multi-modal inference, resulting in accurate 3D body modeling even when the input sensor modality is only a subset of the training modalities. *Equal Contributions |
|
|
In this work, we address this gap by proposing a new technique for regression of human parametric model that is explicitly informed by the known hierarchical structure, including joint interdependencies of the model. This results in a strong prior-informed design of the regressor architecture and an associated hierarchical optimization that is flexible to be used in conjunction with the current standard frameworks for 3D human mesh recovery. *Equal Contributions |
|
|
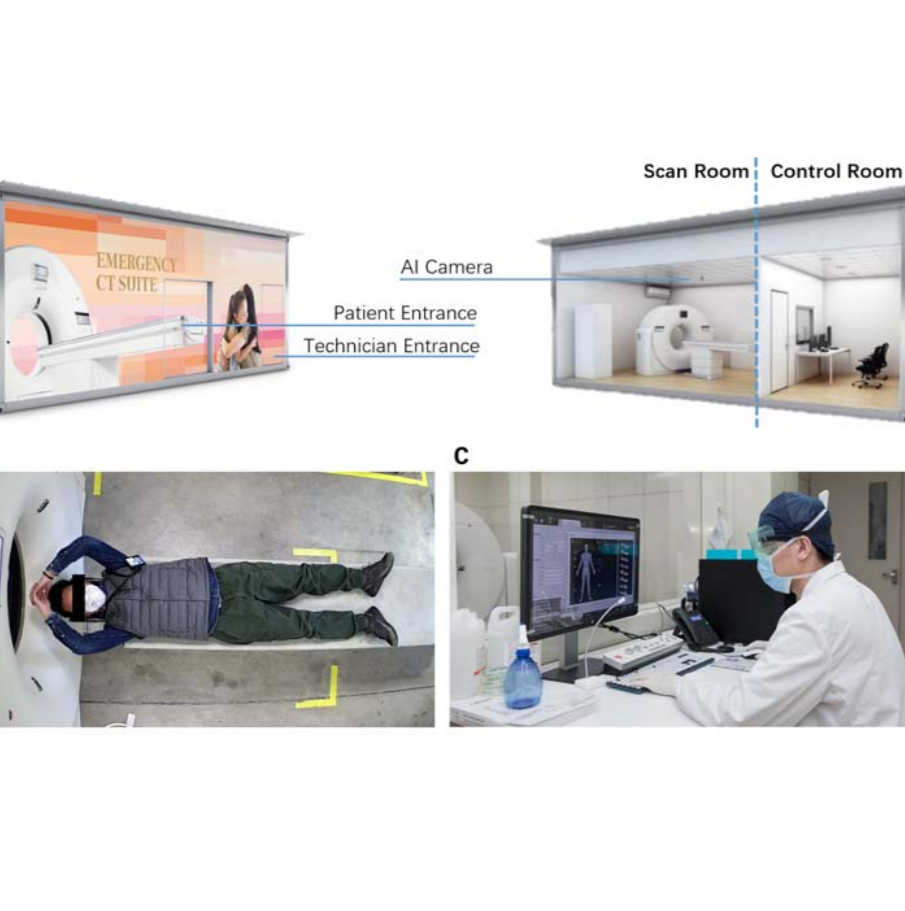
The COVID-19 pandemic, caused by the highly contagious SARS-CoV-2 virus, has overwhelmed healthcare systems worldwide, putting medical professionals at a high risk of getting infected themselves due to a global shortage of personal protective equipment. To help alleviate this problem, we design and develop a contactless patient positioning system that can enable scanning patients in a completely remote and contactless fashion. Our key design objective is to reduce the physical contact time with a patient as much as possible, which we achieve with our contactless workflow. *Equal Contributions |
|
We cover the entire pipeline of medical imaging and analysis techniques involved with COVID-19, including image acquisition, segmentation, diagnosis, and follow-up. We particularly focus on the integration of AI with X-ray and CT, both of which are widely used in the frontline hospitals, in order to depict the latest progress of medical imaging and radiology fighting against COVID-19. *Equal Contributions |
|
|
We propose the first technique to visually explain VAEs by means of gradient-based attention. We present methods to generate visual attention from the learned latent space, and also demonstrate such attention explanations serve more than just explaining VAE predictions. We show how these attention maps can be used to localize anomalies in images, and how they can be infused into model training, helping bootstrap the VAE into learning improved latent space disentanglement. *Equal Contributions |
|
|
We present a method to incrementally generate complete 2D or 3D scenes with global consistentcy at each step according to a learned scene prior. Real observations of a scene can be incorporated while observing global consistency and unobserved regions can be hallucinated locally in consistence with previous observations, hallucinations as well as global priors. Hallucinations are statistical in nature, i.e., different scenes can be generated from the same observations. |
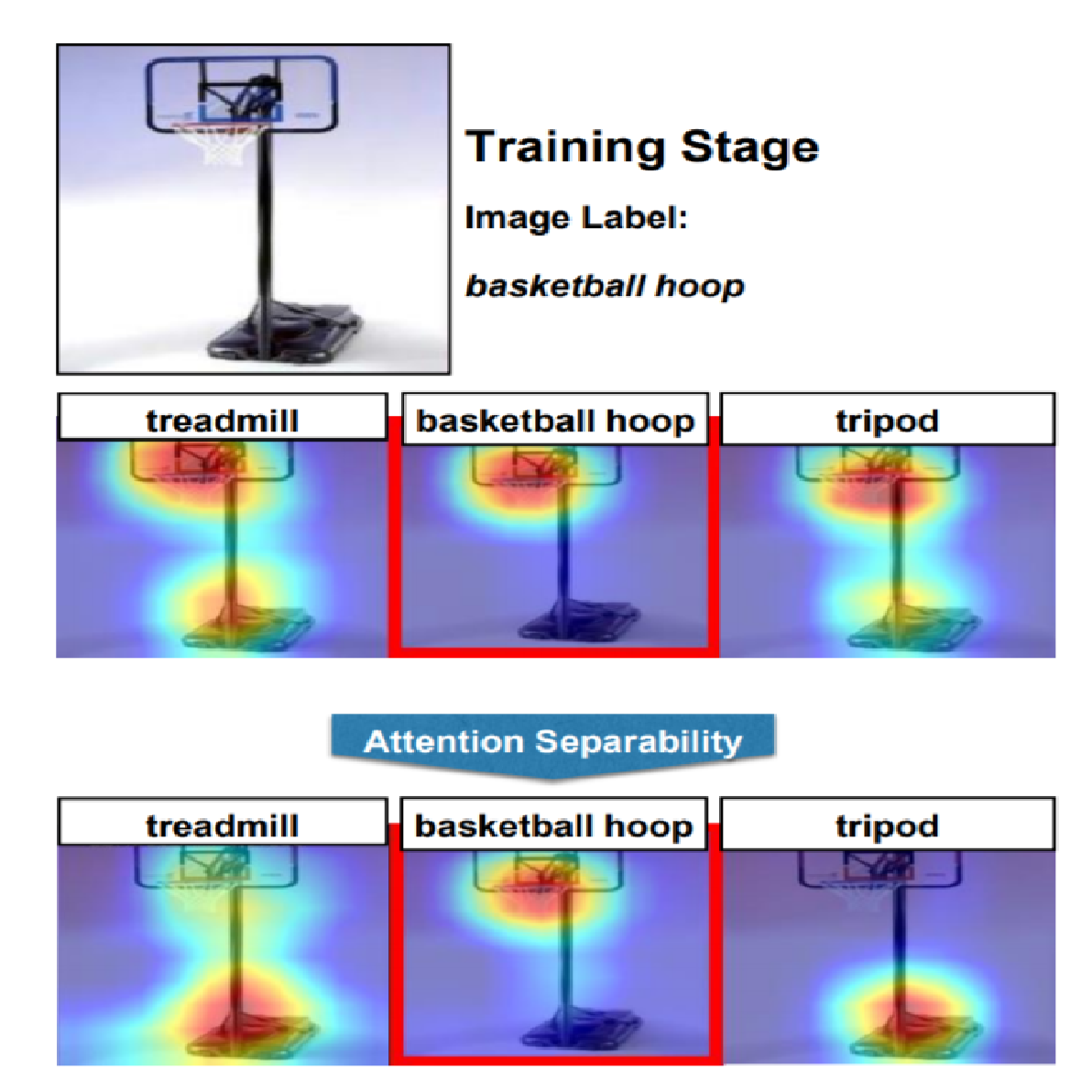 |
We improve the generalizability of CNNs by means of a new framework that makes class-discriminative attention a principled part of the learning process. We propose new learning objectives for attention separability and cross-layer consistency, which result in improved attention discriminability and reduced visual confusion. |
 |
We solve the key problem of existing 3D object pose estimation methods requiring expensive 3D pose annotations by proposing a new method that matches RGB images to CAD models for object pose estimation. Our method requires neither real-world textures for CAD models nor explicit 3D pose annotations for RGB images. |
|
|
This is an extension of our CVPR 18 work with added support of bounding box labels seamlessly integrated with image level and pixel level labels for weakly supervised semantic segmentation. |
|
|
We introduce a pipeline to map unseen target samples into the synthetic domain used to train task-specific methods. Denoising the data and retaining only the features these recognition algorithms are familiar with. *Equal Contributions |
|
|
Knowledge distillation should not only focus on "what", but also "why". We peoposed an online learning method to preserve the exisiting knowledge without storing any data, while making the classifier progressively learn to encode the new classes. *Equal Contributions |
|
|
We proposed the first learning architecture that integrates attention consistency modeling and Siamese representation learning in a joint learning framework, called the Consistent Attentive Siamese Network (CASN), for person re-id. |
|
|
Yash Goyal, Ziyan Wu, Jan Ernst, Dhruv Batra, Devi Parikh, Stefan Lee International Conference on Machine Learning (ICML), 2019 A technique to produce counterfactual visual explanations. Given a 'query' image I for which a vision system predicts class c, a counterfactual visual explanation identifies how I could change such that the system would output a different specified class c′. |
|
|
supplementary / dataset / code We present an extensive review and performance evaluation of single and multi-shot re-id algorithms. The experimental protocol incorporates 11 feature extraction and 22 metric learning and ranking techniques and evaluates using a new large-scale dataset that closely mimics a real-world problem setting, in addition to 16 other publicly available datasets. *Equal Contributions |
|
|
We propose zero-shot deep domain adaptation (ZDDA) for domain adaptation and sensor fusion. ZDDA learns from the task-irrelevant dual-domain pairs when the task-relevant target-domain training data is unavailable. |

|
code by alokwhitewolf / talk In one common framework we address three shortcomings of previous approaches in modeling such attention maps: We (1) first time make attention maps an explicit and natural component of the end-to-end training, (2) provide self-guidance directly on these maps by exploring supervision form the network itself to improve them, and (3) seamlessly bridge the gap between using weak and extra supervision if available. |
|
|
We proposed ConceptGAN, a novel concept learning framework where we seek to capture underlying semantic shifts between data domains instead of mappings restricted to training distributions. The key idea is that via joint concept learning, transfer and composition, information over a joint latent space is recovered given incomplete training data. |
|
|
Related Product: Siemens
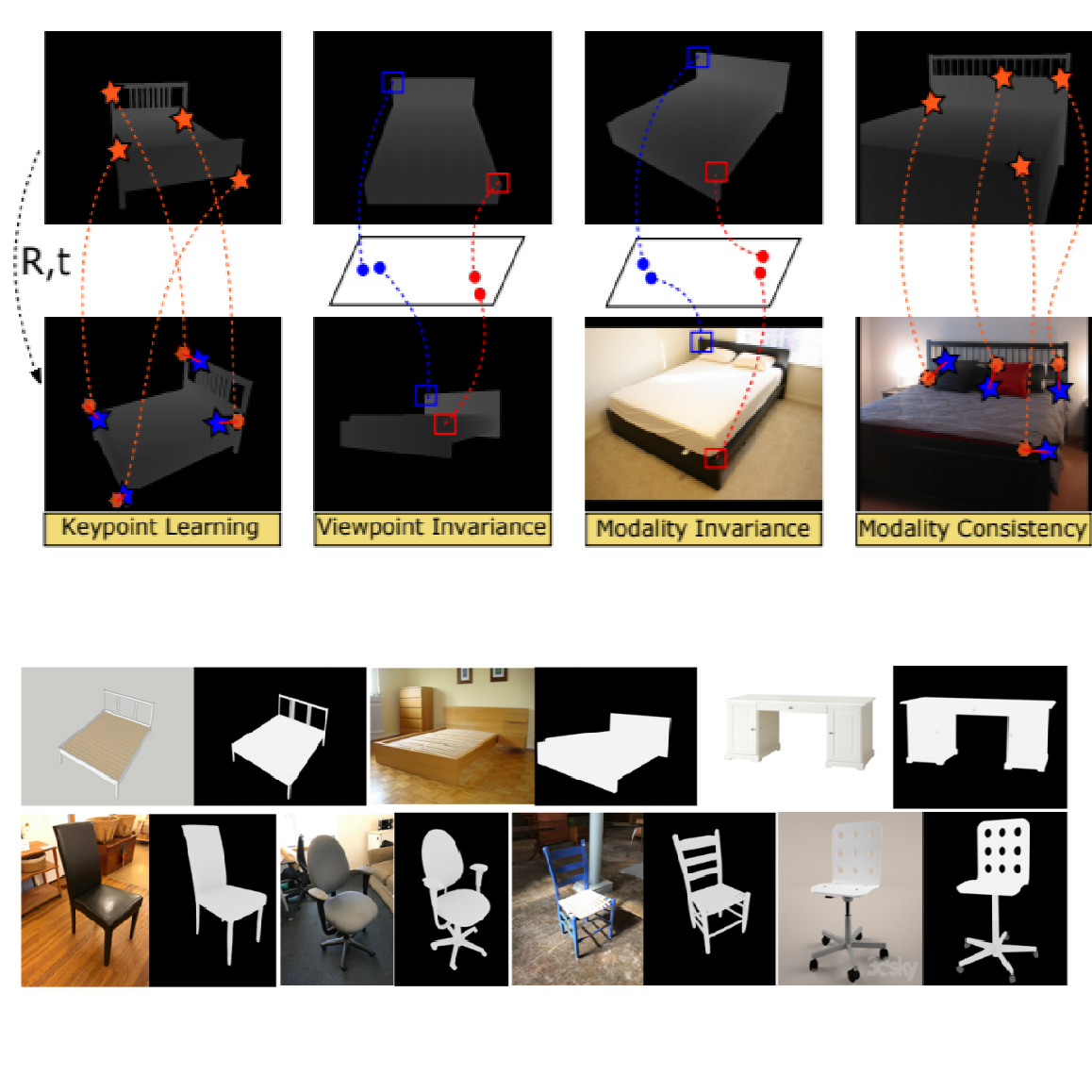
EasySpareIDea® We proposed an end-to-end learning framework for keypoint detection and its representation (descriptor) for 3D depth maps or 3D scans, where the two can be jointly optimized towards task-specific objectives without a need for separate annotations. |
|
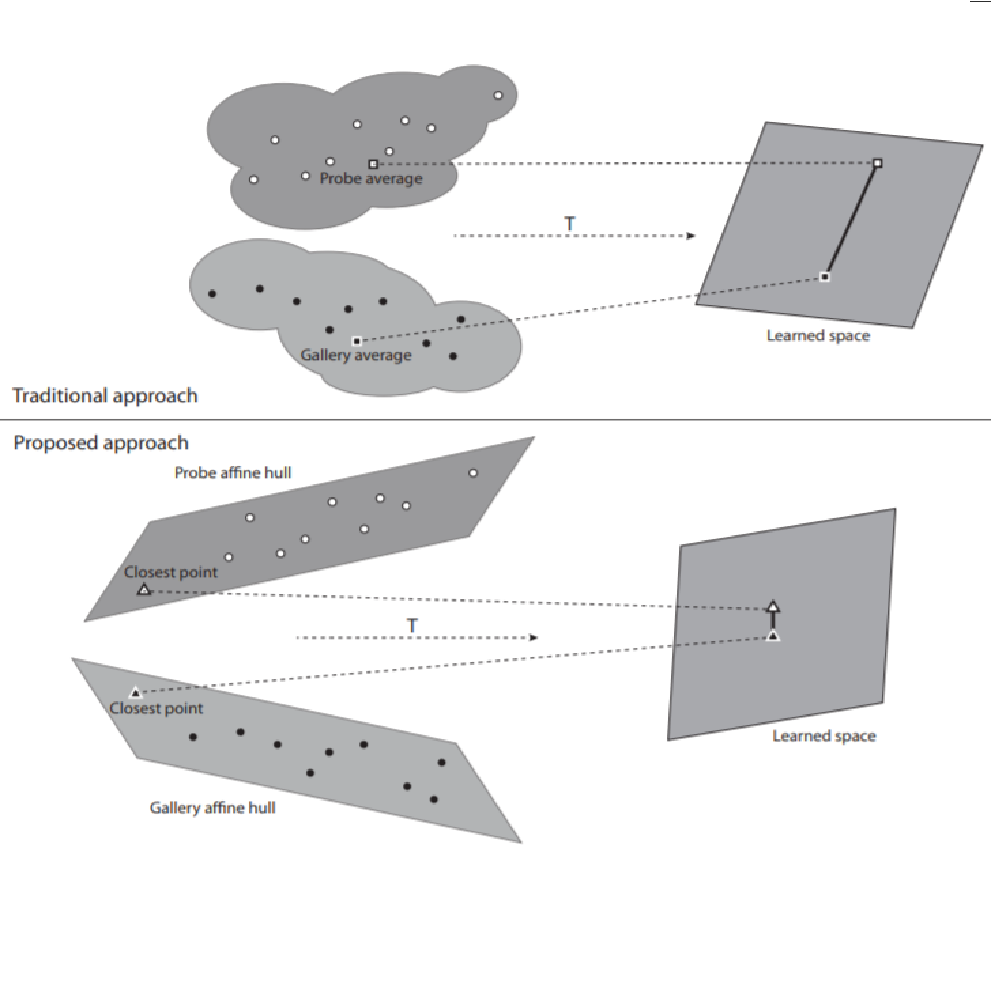
We describe the image sequence data using affine hulls, and we show that directly computing the distance between the closest points on these affine hulls as in existing recognition algorithms is not sufficiently discriminative in the context of person re-identification. To this end, we incorporate affine hull data modeling into the traditional distance metric learning framework, learning discriminative feature representations directly using affine hulls. |
|
|
We propose a novel approach leveraging only CAD models to bridge the realism gap. Purely trained on synthetic data, playing against an extensive augmentation pipeline in an unsupervised manner, a generative adversarial network learns to effectively segment depth images and recover the clean synthetic-looking depth information even from partial occlusions. *Equal Contributions |
|
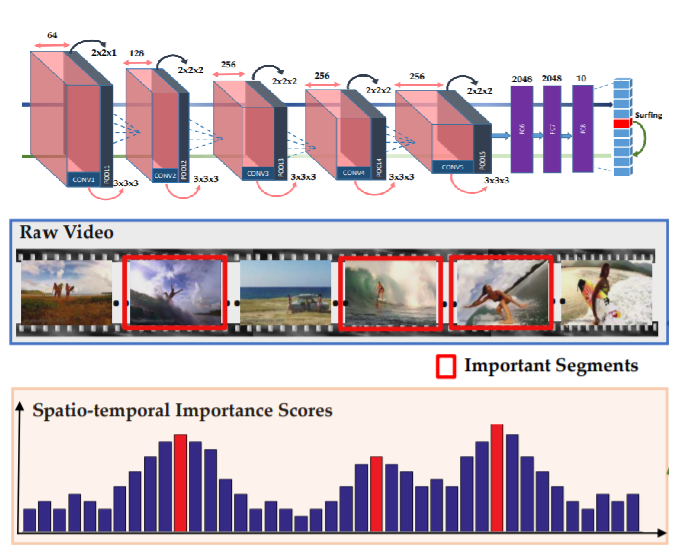
We proposed a weakly supervised approach to summarize videos with only video-level annotation, introducing an effective method for computing spatio-temporal importance scores without resorting to additional training steps. |
|
Related Product: Siemens
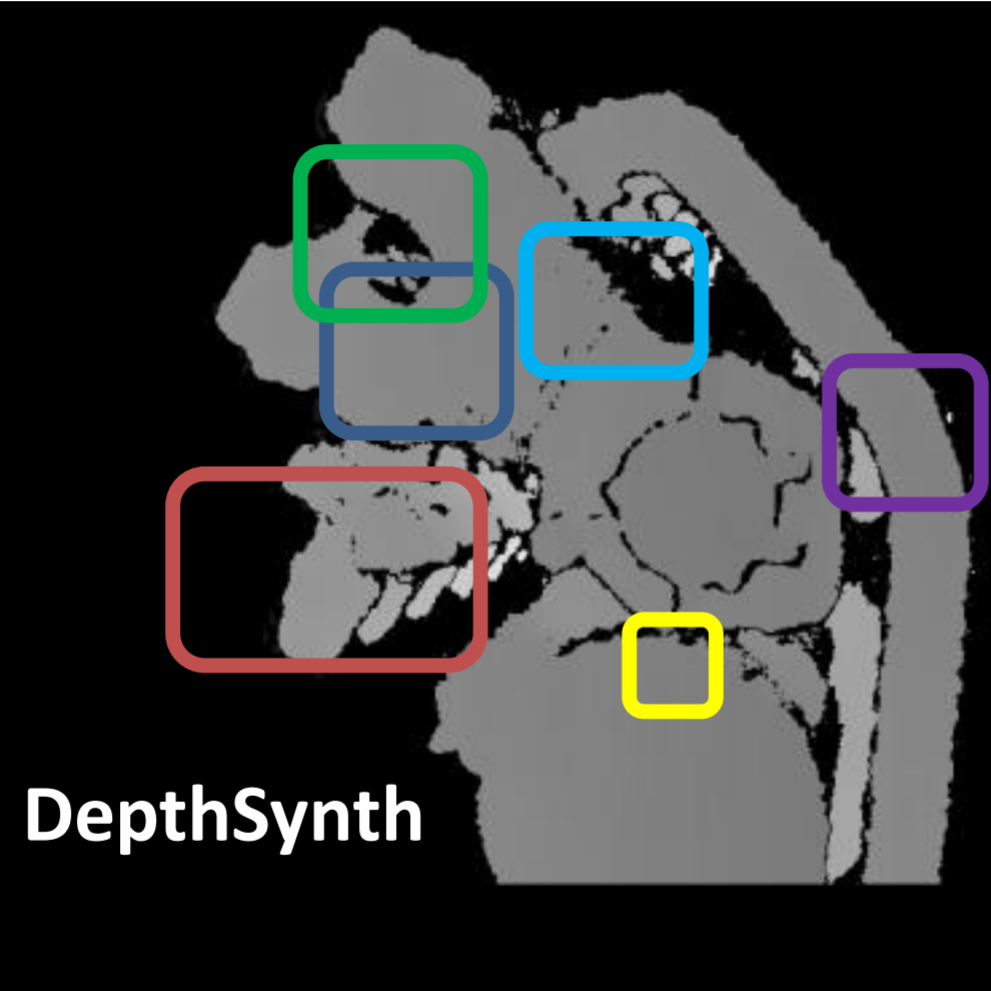
EasySpareIDea® We propose an end-to-end framework which simulates the whole mechanism of 3D sensors (structured light and TOF), generating realistic depth data from 3D models by comprehensively modeling vital factors e.g. sensor noise, material reflectance, surface geometry. |
|
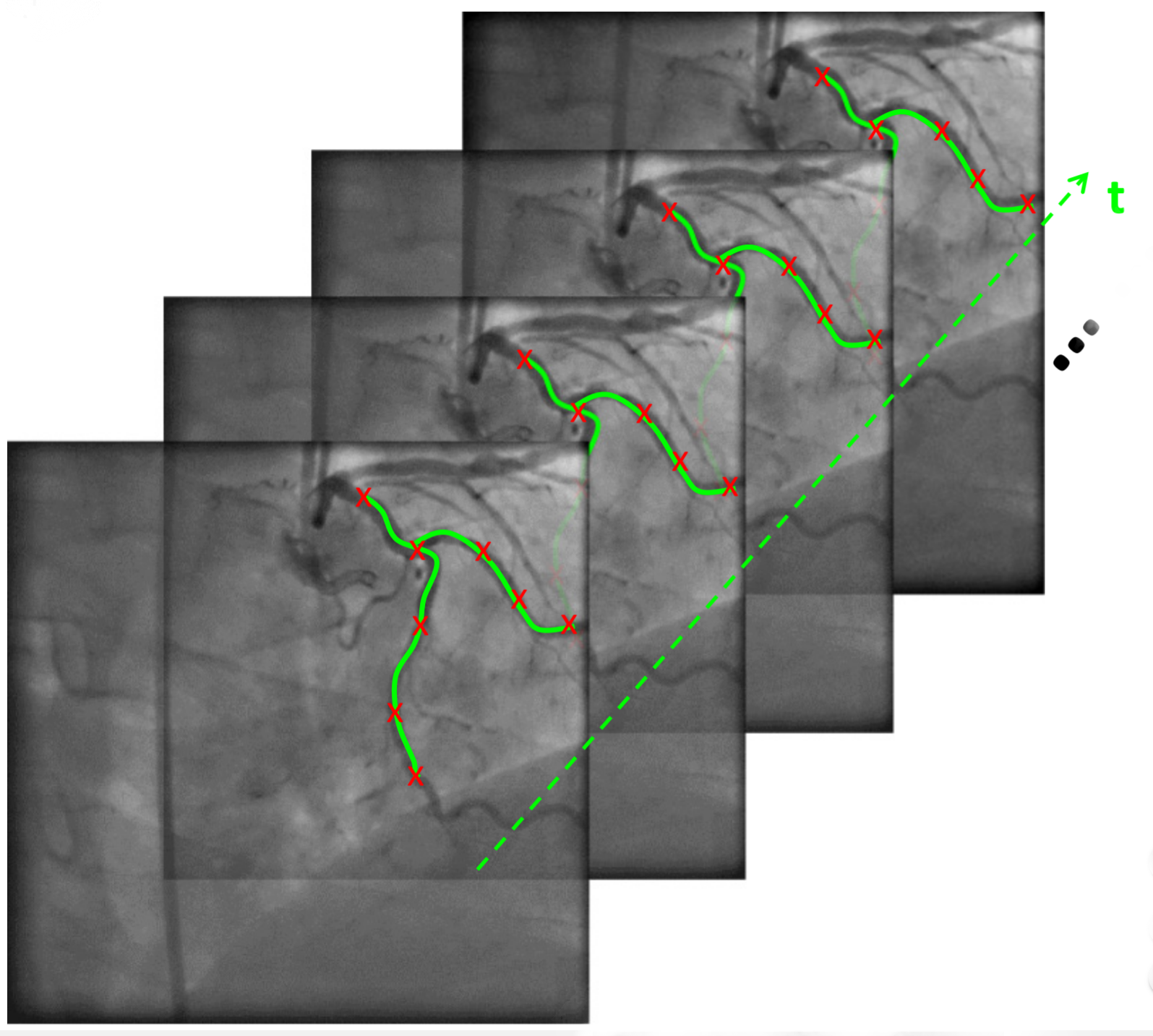
We present a method to track vessels in angiography. Our method maximizes the appearance similarity while preserving the vessel structure. The vessel tree tracking problem turns into finding the most similar tree from the DAG in the next frame, and it is solved using an efficient dynamic programming algorithm. |
|
|
We detail the challenges of the real-world airport environment, the computer vision algorithms underlying our human detection and re-identification algorithms, our robust software architecture, and the ground-truthing system required to provide the training and validation data for the algorithms. |
|
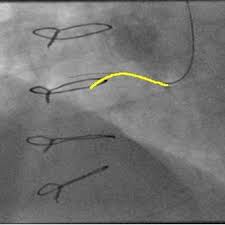
We model the wire-like structure as a sequence of small segments and formulate guidewire tracking as a graph-based optimization problem which aims to find the optimal link set. To overcome distracters, we extract them from the dominant motion pattern and propose a confidence re-weighting process in the appearance measurement. |
|
|
This book covers aspects of human re-identification problems related to computer vision and machine learning. Working from a practical perspective, it introduces novel algorithms and designs for human re-identification that bridge the gap between research and reality. The primary focus is on building a robust, reliable, distributed and scalable smart surveillance system that can be deployed in real-world scenarios. |
|
|
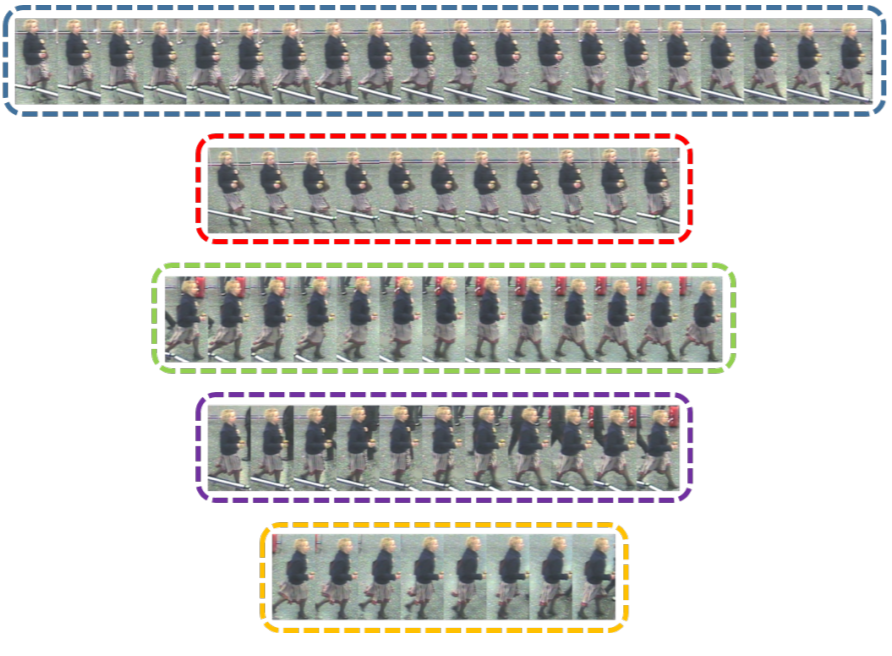
We build a model for human appearance as a function of pose, using training data gathered from a calibrated camera. We then apply this “pose prior” in online re-identification to make matching and identification more robust to viewpoint. We further integrate person-specific features learned over the course of tracking to improve the algorithm’s performance. |
|
We introduce an algorithm to hierarchically cluster image sequences and use the representative data samples to learn a feature subspace maximizing the Fisher criterion. The clustering and subspace learning processes are applied iteratively to obtain diversity-preserving discriminative features. |
|
|
|
|
|
We propose a novel “virtual insertion” scheme for Structure from Motion (SfM), which constructs virtual points and virtual frames to adapt the existence of visual landmark link outage, namely “visual breaks” due to no common features observed from neighboring camera views in challenging environments. |

|
Video surveillance is a critical issue for defense and homeland security applications. There are three key steps of video surveillance: system calibration, multi-object tracking, and target behavior analysis. In this thesis we investigate several important and challenging computer vision problems and applications related to these three steps, in order to improve the performance of video surveillance. |
|
|
This paper addresses the problem of detecting counterflow motion in videos of highly dense crowds. We focus on improving the detection performance by identifying scene features — that is, features on motionless background surfaces. We propose a three-way classifier to differentiate counterflow from normal flow, simultaneously identifying scene features based on statistics of low-level feature point tracks. |
|
|
We discuss the high-level system design of the video surveillance application, and the issues we encountered during our development and testing. We also describe the algorithm framework for our human re-identification software, and discuss considerations of speed and matching performance. |
|
|
We propose a complete model for a pan-tilt-zoom camera that explicitly reflects how focal length and lens distortion vary as a function of zoom scale. We show how the parameters of this model can be quickly and accurately estimated using a series of simple initialization steps followed by a nonlinear optimization. We also show how the calibration parameters can be maintained using a one-shot dynamic correction process; this ensures that the camera returns the same field of view every time the user requests a given (pan, tilt, zoom), even after hundreds of hours of operation. |
|
|
We introduce two novel methods to improve the performance of wide area video surveillance applications by using scene features. |
|
|
We introduce an airport security checkpoint surveillance system using a camera network. The system tracks the movement of each passenger and carry-on bag, continuously maintains the association between bags and passengers, and verifies that passengers leave the checkpoint with the correct bags. |
|
|
Resources are presented for fostering paper-based election technology. They comprise a diverse collection of real and simulated ballot and survey images, and software tools for ballot synthesis, registration, segmentation, and ground truthing. |
|
|
Photocopies of the ballots challenged in the 2008 Minnesota elections, which constitute a public record, were scanned on a high-speed scanner and made available on a public radio website. Based on a review of relevant image-processing aspects of paper-based election machinery and on additional statistics and observations on the posted sample data, robust tools were developed for determining the underlying grid of the targets on these ballots regardless of skew, clipping, and other degradations caused by high-speed copying and digitization. |
| |
| |